Blotting Systems
Blotting Systems
Immunoblot commonly referred to as “Western blot” (WB), is used to detect antibodies to specific epitopes of electrophoretically separated subspecies of antigens. Western Blotting or immunoblotting is to determine the relative amounts of the protein present in different samples, with a specific primary antibody. Development of electrophorteic transfer to a suitable membrane, by Towbin and others (Western Blot) now permits the rapid, efficient and quantitative transfer of protein and nucleic acids to immobilizing media.
In these assays, antigens are first electrophoresed and then blotted onto a piece of filter paper. Thus the filter paper is the solid phase to which the antigen is bound. The filter is
blocked and then reacted with appropriate tagged antibodies and then substrate. Spots can then be detected by immuno blotting. A color reaction indicates a positive test. These spots indicate the position of the protein of interest.
The transfer of electrophoretically resolved DNA, RNA, and protein to an immobilizing paper or membrane matrix has become a standard procedure for the sensitive and specific detection of biologically interesting macromolecules. Exact and reproducible replicas of separations are captured on the paper or membrane sheets. After transfer, antigens, antibodies, hormones, receptor proteins, and glycoproteins can be detected by staining or by specific fluorescent (FIA), enzyme-substrate (EIA), or autoradiographic (RIA) assay.
Western blots allow investigators to determine the molecular weight of the protein and to measure the relative amounts of protein present in different samples.
Western Blotting systems are useful for the transfer of protein samples from SDS-PAGE gel to nitrocellulose membrane support with gel cassette at high current. The cassette is submerged in a buffer tank in between anode and cathode cells.
Dimensions: 16cm(L) x 5cm(B) x 13cm(H)
No. Of Cassettes: 1 (8 x 7cm gel)
Buffer Volume: 300ml

Complete unit consists of
- Basic unit with platinum electrode
- Gel cassette (1 Set)
- Filter pad (Pack of 6)
- Cushion pad (Pack of 6)
- Power cord and Lid (1 no. each)
- User manual
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1246-01 | MEDOX-BIO® Mini Western Blotting System | Set |
Dimensions: 16cm(L) x 12cm(B) x 13cm(H)
No. Of Cassettes: 2 (8 x 7cm gel)
Buffer Volume: 700ml

Complete unit consists of
- Basic unit with platinum electrode
- Gel cassette (2 Sets)
- Filtet pad (Pack of 12)
- Cushion pad (Pack of 12)
- Heat exchanger (1 No.)
- Power cord and Lid (1 No. each)
- User manual
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1247-01 | MEDOX-BIO Mini Dual Western Blotting System | Set |
Dimensions: 18cm(L) x 12cm(B) x 26cm(H)
No. Of Cassettes: 1 (16 x 14cm gel)
Buffer Volume: 1000ml

Complete unit consists of
- Basic unit with platinum electrode
- Gel cassette (1 Set)
- Filter pad (Pack of 6)
- Cushion pad (Pack of 6)
- Power cord and Lid (1 No. each)
- User manual
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1248-01 | MEDOX-BIO® Midi Western Blotting System | Set |
Dimensions: 18cm(L) x 15cm(B) x 22cm(H)
No. Of Cassettes: 2 (16 x 14cm gel)
Buffer Volume: 1500ml
Complete unit consists of
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1248-02 | MEDOX-BIO® Midi Dual Western Blotting System with Water Circulation | Set |
Dimensions: 18cm(L) x 12cm(B) x 13cm(H)
No. Of Cassettes: 2 (8 x 7cm gel)
Buffer Volume: 700ml
Complete unit consists of
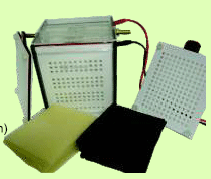
- Basic unit with platinum electrode
- Gel cassette (2 Sets)
- Filtet pad (Pack of 12)
- Cushion pad (Pack of 12)
- Heat exchanger (1 No.)
- Power cord and Lid (1 No. each)
- User manual
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1247-01 | MEDOX-BIO® Mini Dual Western Blotting System | Set |
| Cat. No. | Product | Unit |
MEDOX-BIO WESTERN BLOTTING SYSTEMS | ||
| MX-1246-02 | Scotch Brite Pads 8 x 7cm gel | 6/pack |
| MX-1246-03 | Cushion Pads 8 x 7cm gel | 12/pack |
| MX-1246-04 | Scotch Pads 16 x 14cm gel | 6/pack |
| MX-1246-05 | Cushion Pads 16 x 14cm gel | 12/pack |
Dimensions
17cm(L)x17cm(B)x9cm(H)
Buffer Volume: 50ml
Complete unit consists of

- Basic unit with Graphite Electrode
assembly (2 Nos.) - Insulation Sheets (2 Nos.)
- Power cord (1 No.)
- User Manual
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1249-01 | MEDOX-BIO® Mini Semi Dry Blotting System (10X10cm gel) | Set |
Dimensions
27cm(L)x27cm(B)x9cm(H)
Buffer Volume: 150ml
Complete unit consists of

- Basic unit with Graphite Electrode
assembly (2 Nos. - Insulation Sheets (2 Nos.)
- Power cord (1 No.)
- User Manual
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1249-02 | MEDOX-BIO® Midi Semi Dry Blotting System (20X20cm) | Set |

| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1295-01 | MEDOX-BIO® Mini Semi Dry Blotting System Advanced (10X10) | Set |

| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1295-02 | MEDOX-BIO® Mini Semi Dry Blotting System Advanced (20X20) | Set |
Dimensions
20cm(L)x10cm(B)x7cm(H)
Buffer Volume: 300ml
Complete unit consists of
Basic unit (1 No.)
Weight (1 No.)
User Manual
| Ordering Information | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1238-01 | MEDOX-BIO® Southern Blotting System | Set |
| Accessories | ||
| Cat.No | Product | Units |
| MX-1246-02 | Filter Pads 8x7cm gel | 6/pack |
| MX-1246-03 | Cushion Pads 8x7cm gel | 12/pack |
| MX-1246-04 | Filter Pads 16x14cm gel | 6/pack |
| MX-1246-05 | Cushion Pads 16x14cm gel | 12/pack |

